Ep#30 Season 4 Heart of Conservation Transcript (Edited)
Read or Listen. All paintings-photos courtesy Sudarshan Shaw.
0:05
Lalitha Krishnan: I’m Lalitha Krishnan and you’re listening to episode #30, season 4 of Heart of Conservation. I bring you stories from the wild that keep us all connected to the natural world.
For someone who has no sense of direction and couldn’t probably read a map to save her life, I have to say I practically drooled over one visually delightful map that I came across on Instagram. It conveyed a spectacular visually-rich story of a place, its people and art and biodiversity on a single sheet. This is one, I would easily put up on my wall permanently. I will be putting them up on my blog, Earthy Matters very soon, so do have a look.
My guest today is not a cartographer by profession but a young, extremely talented visual artist from NIFT, whose keen sense of perception and belonging, passion for depicting, and preserving local art, and love for natural history is tangible in his stunning artworks which go way beyond creating maps. I am speaking to one of India’s rising young, inspiring artists and authors, Sudarshan Shaw. Welcome to Heart of Conservation Sudarshan. Thank you for joining me.
1:19
Sudarshan Shaw: Thank you so much for having me on Heart of Conservation Lalitha. It’s an absolute honour to be here.
Lalitha Krishnan: My pleasure. Sudarshan why don’t we start by you telling us a little bit about yourself and what influences your work?
Sudarshan Shaw: I was born and brought up in the culturally rich cities of Bhubaneshwar and Kolkata. And I grew up feeding on art forms and colours of all types. And, I have always been a history buff so… all of which came together after I discovered my calling towards wildlife while I pursuing my final year of college. That’s when I visited Ranthambore National Park which was my first ever formal introduction to the wild world. It was also for my graduation project and while the forest look all great and beautiful, I always felt that connection was missing; some sort of connection. Thus, I started to explore more and more regions to understand myself and the situation better and have a better understanding of the wider world.
2:25
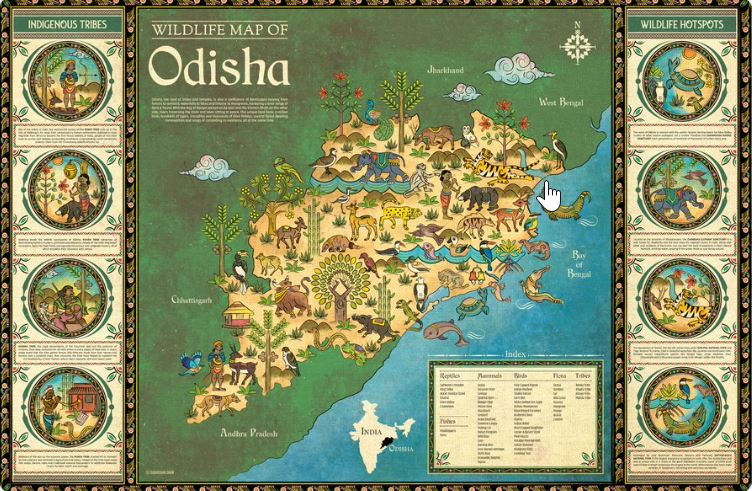
Lalitha Krishnan: Nice. Let’s talk briefly about all the maps you created. You created more than one for Orissa, biodiversity maps for Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajasthan and West Bengal, a special Elephant corridor one for Kerala and other clients like the one for the Shiv Nadar University etc. The first one which is the wildlife map of Orissa- your home state was self-funded. Am I right? What I love about that map is how you incorporated the local tribes and hotspots in the traditional pattachitra style of Orissa. It almost feels like a tribute. So, what made you create this one?
3:13
Sudarshan Shaw: Yes, it is a tribute indeed. It’s a tribute to the land, the wild and the cultural heritage of my state. It’s also a tribute to the strong relationship among them that enhances their meaning of each other. I always felt a huge disjoint in the natural and cultural heritage of India and the kind of graphic language the young communicators use in the country. I feel it is heavily influenced by the west and does not have that connection with the native land and hence it’s not acceptable to the masses in a certain way. So, the vibrance and diversity that folk arts have in store have disappeared from the contemporary visual language that we used to in recent time used to communicate our stories. This was my humble attempt to bring it back with all dignity and pride. Another reason would be Odisha itself. Odisha has an abundance of wildlife. We almost know all the stories regarding Odisha but it never found a place, I mean materially in our surroundings.
What I saw is the pattachitra paintings which are quite prevalent in Odisha -which is the folk-art form in Odisha – and it has a place in our homes over here. There are depictions of gods and goddesses and many other folklores on the walls. I thought this could give me an important platform if I drew it in that style and I depicted wildlife in that style. Eventually, it worked out well and the wildlife map found a place in people’s homes. So, they put it up where they used to put pattachitra paintings.
5:00
Lalitha Krishnan: That’s such an honour. That’s fantastic. What is your creative process? How do you create a map-I don’t mean technically- but I want to know how you think you know, and how long it takes, who commissions these maps. How does it work?
5:23
Sudarshan Shaw: The process usually starts with intense research, which is both online and in the field. It’s quite impossible to do justice to ….(lost in translation) with short timelines or deadlines. So, I try my best to gather as much as I can; so more of essence than information. I must say, the internet has negligent information on this so most of the interaction and interpretations have travelled orally with tradition or in folk art forms. So, the idea is to go through and explore as many of these. The next step is where Is it down to innovate a graphic style which is more often inspired but local art and traditions. Then, I design a layout and then spend about one to two months to complete/render it depending on the amount of details. Most of these maps have been funded by the forest departments of various states or other wildlife NGOs if not other private institutions.
Lalitha Krishnan: Great. Being from Odisha, does practising the traditional art of Odisha come naturally to you? Is it something you learnt as a child or is it something that you learnt in art school?
6:45
Sudarshan Shaw: Naturally it was in my subconscious because we’d always be looking at these art forms on stone sculptures, wall paintings of different buildings in Odisha and also in homes, as I said earlier. But, consciously I started practising and grasping it after I visited Ranthambore wherein I first had that interaction with Phad paintings of Rajasthan. There are these common folk paintings of Rajasthan, wherein they had drawn stories from the wild in their artworks. For example, in the story of ‘Machhli’ the Tiger, wherein they had depicted the tiger in a very beautiful style in stories from its birth to its death and everything. This was the main reason why I started grasping art forms more and this is how I implemented it. I get a story from one place and try to incorporate the folk-art of that place into it (the art).
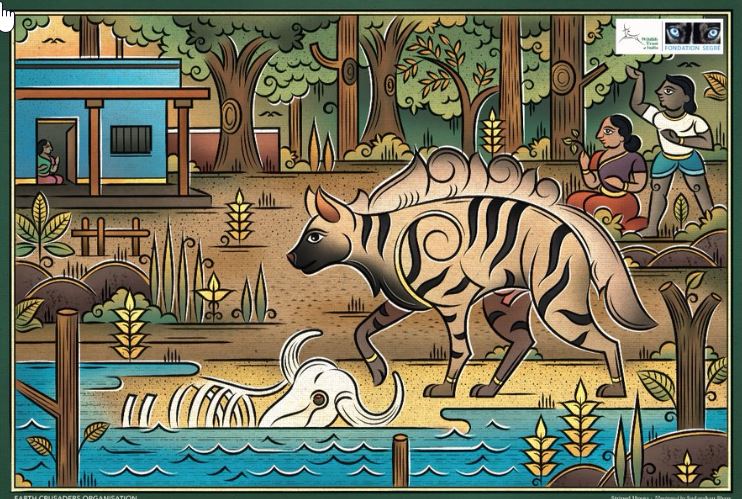
Lalitha Krishnan: O.K. That’s very sensitive and thoughtful of you to do that. You have depicted wildlife, for example, the striped hyena, otters etc that are also listed as endangered or vulnerable by the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) Tell us something about these. I love the little camera trap you have put along with the ‘Black tiger’, the pseudo-melanistic black tiger painting of yours. I don’t know if the Fishing cat’ (see podcast cover) is part of this series but that too just caught my eye.
8:27
Sudarshan Shaw: The Fishing cat was the first painting that I did for this series but that was also a self-funded one. The main idea always starts with a self-funded one and the Fishing cat was one of those. The idea behind drawing the Fishing cat was–which is also a mud painting by the way—during that time, I heard a lot about fishing cats. You know they are found on the outskirts of my hometown. It was very interesting to know that these kinds of creatures live nearby. So, I started looking at images of fishing cats in Odisha and West Bengal and other regions of India. I found images of fishing cats which are mostly nocturnal. The images were quite similar. Once I got a glimpse of a fishing cat drawn in the Kalighat form of painting in Bengal, and I saw a very distinct flavour to it. That cat was depicted holding a fish, it had a stance of its own and it almost looked like that fishing cat is Bengal and it was very different from that of Odisha or any other region of the world. So, a depiction of that species in that art form you know helped in sensitising the people of that particular region regarding that species. That was my whole idea. To incorporate that style and show the world that all these creatures have their distinct characters from the places that they belong to. That was my main idea behind that. The other artworks: the Smooth-coated (otters), the (striped) hyena, you know, they tagged along, people understood my reasoning behind the Fishing cat and they wanted similar species to be shown in their own characters so that they would help in spreading awareness and in sensitising people about the species.
10:30
Lalitha Krishnan: It’s true when you say, (species) have their own stance, their own character of the place. That’s an interesting take. You know, tigers have been part of the Indian psyche forever and they feature a lot in your paintings. I saw one of The 9 Tigers depicted in different folk styles which tells us so much in one go.
I also want to talk about the ‘Tiger Boundary’ piece which is nothing short of mesmerising.
I like that you said somewhere that the boundary in the frame instead of blocking in gives you the artist and the subject, in this case, the tiger, free reign. Did I get that right? What do you mean by that? And what draws to the tiger?

11:17
Sudarshan Shaw: Absolutely. Apart from being as popular as ‘T’ for Tiger, and one of the epic predators of the forest systems in India, I feel tigers are truly beautiful beings in all senses. They are as gentle as they are fierce, the air of pride and mystery around the creature makes them much larger than their actual size -which is both inside the forest and outside. So, what draws me and the whole forest and nation to the tiger are that it’s like another mystery. I never met a tiger in the wild. But fortunately, I met so many in folk art and in my imagination and they are all different from each other.
So, yes, as an artist I always felt conflicted about having boundaries around my artworks. On the face, the borders look like confinements, a kind of limitation but they are very common, if you observe, in all the folk-art forms of India. So, one fine day, during an interaction with a pattachitra folk artist, he was explaining to me why they drew borders on the canvas before they started the painting inside. That was the instance when I thought that is how tigers also mark the territories for themselves in the forest and both the artist and tiger would then paint their minds and live inside it. I could then understand how boundaries set by self, bring a sense of safety, depth of connection and commitment to our responsibility. All of which actually sets us free.
12:56
Lalitha Krishnan: Wow. That’s all I can say. You authored your first children’s book called “When a Forest Wakes up”. Congratulations. The name itself evokes a visual flood but the book is also very magical. Your interpretation of nature… where trees are antlers sending messages and elephants block out the sun and birds fly to flowers in gratitude for the colours and where hills are sleeping rhinos…it’s so wonderous and I can just imagine the wonder and oneness that any child will love. I believe you said, “The basic idea of the book is ‘breaking definitions”. Yes?
13:41
Sudarshan Shaw: yes, one of the ideas behind the book was to see beyond rigid definitions that we have set for ourselves. To dive into a world of imagination and the endless possibilities that it has for us. So, another idea behind the book was actually inspired by animism. A belief system by the various ancient indigenous communities in India, according to which everything from the stones to the mountains to the trees and rivers are living forces and beings bigger than us or just like us. All of these live in relation to each other.
I remember how we were taught in our school days that nature is full of resources and had multiple uses for us humans. And the distinction between biotic and abiotic, the living and non-living things. We have been told to see a river or soil as a non-living resource it would be very difficult to respect and have a relationship with them. This book is an attempt to change that perception from a very young age.
14:47
If I give you another example, of it, when we ask a child to see towards the sky and the clouds, they would always say the clouds look like different animals or objects and everything. Suddenly, with time, you’d see how the animals and the various objects turn towards being a single cloud. When you ask an adult, what is that they would say, “That’s a cloud. Either it’s going to rain or not going to rain. But when you ask the child, “That is a tiger”. “That’s a leopard…that’s a dinosaur” and whatnot. All those imaginations with time are suppressed and you know, along with the coming of rigid definitions, that ends it for us. So, I wanted to break that stereotype fear out of understanding and definitions.

15:38
Lalitha Krishnan: You’re freeing my mind as you speak. So, I believe you have travelled to Uttarakhand–that’s where I live mostly–and walking in the forests there impacted you. How was it different and is that where you got your studio name. ‘Kyari’ from?
15:56
Sudarshan Shaw: Yes. Uttarakhand has been like a second home. I have travelled to Uttarakhand quite frequently as much as I could. You know, I was in college in Delhi so Uttarakhand wasn’t so far from there. Living there, you can totally understand how special the land is. It is almost beaming with life and beauty, to say the least, and ‘Kyari’ is a very small village near Ram Nagar in Uttarakhand and my studio name lends its name from it and the meaning of it; you know how kyari is a small nursery kind of thing where in they put up small plants and flowers. Then they grow wild from it. That’s the main philosophy of starting my studio wherein I’d be experimenting with different forms and art styles, and stories and those would be going into the wide world.
16:52
Lalitha Krishnan: A nursery of ideas. Lovely
16:54
Sudarshan Shaw: A nursery I would say is one of my best teachers of all the ways I see the world and understand the world the studio is a lifelong tribute to that.
17:05
Lalitha Krishnan: I’d like to know briefly about the ‘My Pictures of Divinity’ series your visual stories about the turtle and sea, and the vulture and the dead e.g. though steeped in lore and also educating us about the animals’ role in the world and their vulnerability today.

17:26
Sudarshan Shaw: Yes, I strongly believe that existence has its meaning in relation and not in isolation. So, my picture of divinity is the search for that godliness that lies in the relationship between the humble life forms that we see and the magnificent ecosystems of sustenance that surround them. So, it is an attempt to override conventional portraits of God that centralised humans while all the legendary powers that they invented were inspired by the ways of the wild. So, it’s a tribute to our true ancestors, the teachers, the deities of the art of thriving and surviving. So, e.g.
I’d say, Uttarakhand and Odisha have been my main source for drawing this series. One story would be the Olive Ridley Turtles of the Odisha coast. If people talk about the species, they talk about the species in isolation but if you actually get to experience that place, you would see how the species is actually a connection between the land and the sea. It’s tying both of them together. That’s the beauty of seeing things in relation and not in isolation. –Sudarshan Shaw
18:40
Lalitha Krishnan: Beautifully put. Coming to my last question, could you share a word, concept or something you believe is important—you’ve mentioned a lot of things—something for all of us to know or imbibe.
18:59
Sudarshan Shaw: Sure. So, being an artist, I’ll say a few lines on how we understand art and nature. For me, art and nature are two sisters of the same fate. Nature has been an inseparable part of native peoples’ being. Folk art has also been practised routinely by all in different ways and forms. So once, the colonial influences came, they alienated our art as a speciality which was quite pristine, exclusive and polished and very far away from us. They did the same to nature and wilderness which became (lost in translation). Art is the nature of all living beings; we must understand this. And, separating them in our words and worlds may have separated us from our true selves and denied us access to the strongest relations which are nature and art. So, I believe we can turn folk art for the reunion and reassurance for everybody, which is free too, we must draw, sing and dance to ourselves and our surroundings better.
20:14 So true, Sudarshan, thank you so much. You’re going to go a long way and all the best for your journey ahead. I am so touched by everything you’ve said and everything you do. Thank you
20:29
Sudarshan Shaw: Thank you so much Lalitha.
Lalitha Krishnan: I hope you enjoyed this episode of Heart of Conservation. Do check out Sudarshan’s artworks. You might want to buy, commission it or gift it to somebody else or yourself. The transcript for this show will be out very soon on Earthy Matters (my blog). You can listen to Heart of Conservation on several platforms so check it out and spread the word, guys. Thanks.
Birdsong by hillside resident, the collared owlet.
All photos courtesy Sudarshan Shaw including Fishing Cat. Podcast cover artwork by Lalitha Krishnan
Disclaimer: Views, thoughts, and opinions expressed in the podcast and show notes belong solely to the guest featured in the episode, and not necessarily to the host of this podcast/blog or the guest’s employer, organization, committee or other group or individual.